British Standard Fitting
BSP / BSPT Hydraulic Fittings
BSP thread stands for British Standard Hydraulic Pipe, british hydraulic fittings and is common in Australia and the commonwealth countries. It is based on trade size rather than actual diameter which can lead to some confusion when measuring ports.
There are two types of BSP threads Hydraulic Fitting;
- BSPP - Female & male thread are both (also known as G), it refers to parallel or straight threads.
- BSPT - Female thread is parallel and the male thread is tapered (also know as R/Rp) (the female thread can also be tapered, these are fairly rare to find). Within BSPT it is also common to call the female thread BSPP (parallel) and the male BSPT (tapered) even though they are both technically a BSPT thread form (the female would be parallel and the male would be tapered).
Both threads hydraulic fitting have the same pitch, angle (55 degrees) and shape (rounded peaks and valleys).
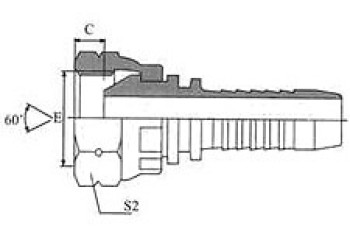
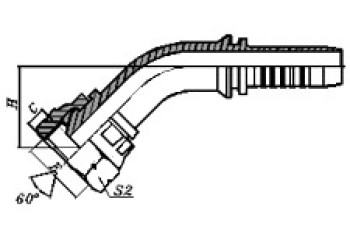
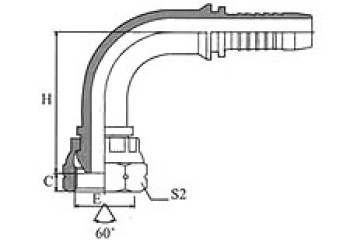
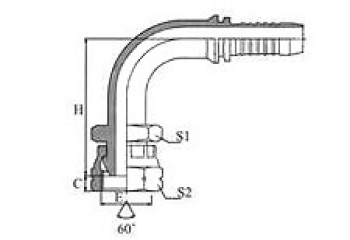
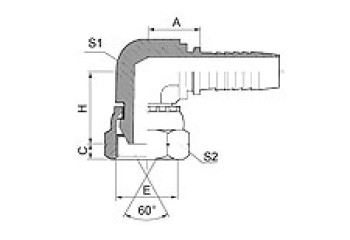
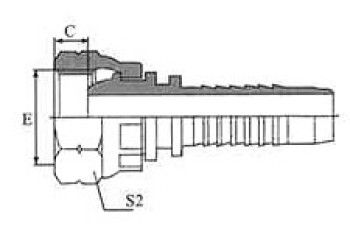
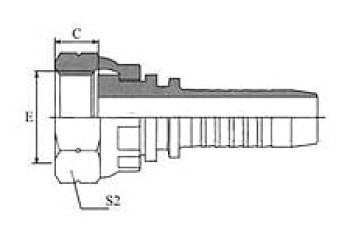
BSP 60° Cone Seal
|
|
|
|
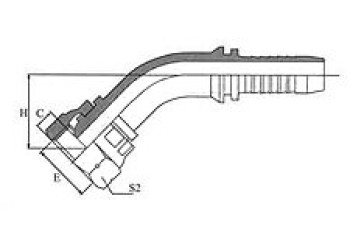
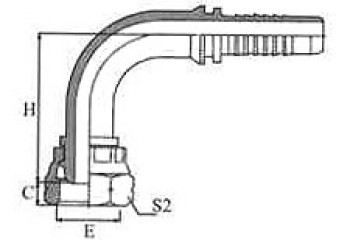
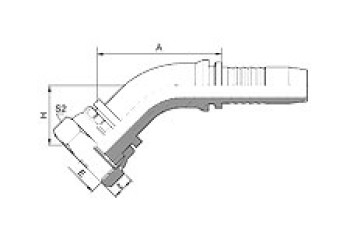
| BSP FEMALE 60º CONE | 45° BSP FEMALE 60º CONE | 90º BSP FEMALE 60º CONE | BSP Female 60º Cone Double Hexagon |
22611/22612 | 22641/22642 | 22691/22692 | 22611D/22612D |
|
|
|
|
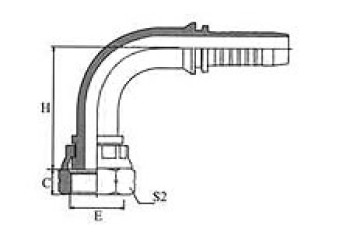
| 90º BSP FEMALE60º CONE DOUBLE HEXAGON | BSP FEMALE 60°CONE DOUBLE HEXAGON | BSP MALE 60º CONE SEAT | BSP MALE DOUBLE USE FOR 60º CONE SEAT OR BONDED SEAL |
22691D/22692D | 22691K/22692K | 12611/12612 | 12611A/12612A |
BSP Multiseal
|
|
|
BSP FEMALE MULTISEAL | 45º BSP FEMALE MULTISEAL | 90º BSP FEMALE MULTISEAL |
| 22111/22112 | 22141/22142 | 22191/22192 |
BSP FLAT SEAT
|
|
|
| BSP FEMALE FLAT SEAT | 45º BSP FEMALE FLAT SEAT | 90º BSP FEMALE FLAT SEAT |
| 22211/22212 | 22241/22242 | 22291/22292 |
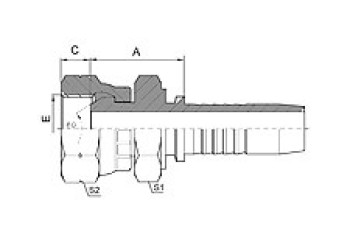
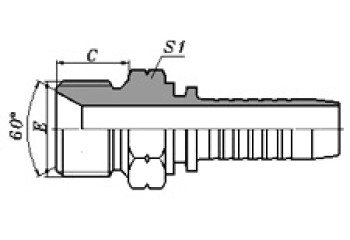
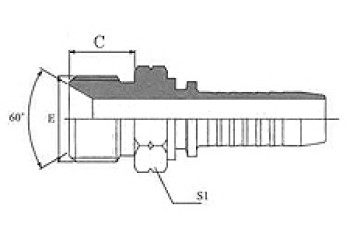
BSP O-Ring Seal / BSPT Male
|
|
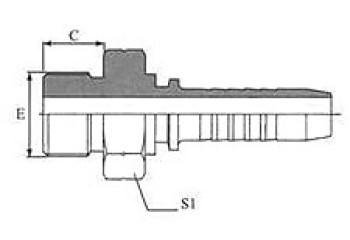
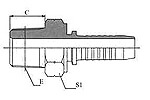
| BSP O-Ring Seal | BSPT Male |
| 12211/12212 | 13011/13012 |
How to order Hose Fitting
Example:Fitting series is P15611,fitting thread is Z1/2"×14,hose bore is 12mm,and is made of carbon steel the number is P15611-08-08,if made of stainless steel,the number is P15611-08-08SS.
Note:1.For use with braided hoses.2.If use with spiral hoses,the fifth number of hose fitting series change from "1" to "2",for example: from P26711-**-** to P26712-**-**
| MATERIAL | CARBON STEEL | COPPER | STAINLESS STEEL |
| SIGN | BR | SS |
| HOSE DN | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 64 |
| HOSE DASH | -01 | -02 | -03 | -04 | -05 | -06 | -08 | -10 | -12 | -16 | -20 | -24 | -28 | -32 | -40 |
| HOSE DASH | 02 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 08 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 32 |
| BSP THREAD | G1/8"×28 | G1/4"×19 | G3/8"×19 | G1/2"×14 | G5/8"×14 | G3/4"×14 | G1"×11 | G1.1/4"×11 | G1.1/2"×11 | G2"×11 | |
| BSPT THREAD | R1/8"×28 | R1/4"×19 | R3/8"×19 | R1/2"×14 | R3/4"×14 | R1"×11 | R1.1/4"×11 | R1.1/2"×11 | R2"×11 | ||
| NPT THREAD | Z1/8"x27 | Z1/4"×18 | Z3/8"×18 | Z1/2"×14 | Z3/4"×14 | Z1"×11.5 | Z1.1/4"×11.5 | Z1.1/2"×11.5 | Z2"×11.5 | ||
| JIC THREAD | 7/16"×20 | 1/2"×20 | 9/16"×18 | 3/4"×16 | 7/8"×14 | 1.1/16"×12 | 1.5/15"×12 | 1.5/8"×12 | 1.7/8"×12 | 2.1/2"×12 | |
FLANGE SIZE | 1/2" | 3/4" | 1" | 1.1/4" | 1.1/2" | 2" |
Hydraulic hose fittings are necessary when connect various conductors such as tubes, pipes, and hydraulic hoses in the hydraulic system. Most of connections pipe fittings have a male and female component to accommodate the connection and assist with the process of containing and directing the flow of fluid. Also it can prevent any leakages and maintain pressure in the hydraulic system. Consequently, hydraulic fittings need to be strong, versatile, and reliable to operate safely and effectively in their respective applications. So hose fittings typically adhere to strict standards which dictate fitting construction, dimensions, and pressure ratings. Our Jinchi fitting factory are hose supplier and supplier different hydraulic fitting types(custom fitting, flare fittings,JIC fittings, NPT fitting, parker hydraulic fittings, push lock fittings, flared fitting, BSPP fittings, metric hydraulic fittings, bsp fitting, ptfe fitting, stainless steel fittings, SAE fittings, reusable hydraulic hose fitting, swivel pipe fitting).
Types of Fittings
1. Connection Type Fittings
Hydraulic fittings are attached via a number of different connection methods, each with its own conveniences and advantages.
2. Compression Fittings
Compression fittings include all types of fittings which use compressive force to connect the vessel to the fitting.
1)Standard compression fittings use metal gaskets, rings, or ferrules which form a seal on the vessel through compression. The compression is typically made by tightening a nut onto the fitting over the piping and ferrule, compressing, and securing the vessel inside. Standard compression fittings do not require tools to assemble, making them convenient for quick field installations.
2)Bite-type fittings are compressive fittings with a sharpened ferrule that "bites" the vessel when compressed and provides the seal. Bite-type fittings, like standard compressive fittings, require no special tools to assemble, but provide a stronger, higher pressure connection.
3)Flare fittings consist of a body with a flared or coned end. Special flaring tools are used to install the vessel inside the flared end, providing a deep seal. Flare fittings can handle higher pressures and a wider range of operating parameters than standard compression fittings.
3.Crimp Fittings
Crimp fittings involve placing hose over a tubular end and crimping against it with a sleeve, ring, or crimp socket. These fittings typically require crimping tools or machines to make the connections.
4.End Fittings
End fittings provide specific surfaces for connecting vessels in hydraulic systems. Plain ends are fittings with surfaces which allow pipes or tubes to be connected by adhesive, solder, welding, or other permanent means. Welding, when done properly on compatible materials, provides a strong and reliable connection.
5.Flange Fittings
Flange fittings are rims, edges, ribs, or collars with flush surfaces perpendicular to the attached pipe or tube. These surfaces are joined and sealed via clamps, bolts, welding, brazing, and/or threading.
6.Push-to-Connect
Push-to-connect fittings have ends that are designed to accept tubing by pushing it into the end. These fittings typically disconnect via some type of collar retraction. These connections are convenient for sections of the system requiring frequent disconnection and reconnection.
7.Threaded Fittings
Threaded fittings have screw threads (built-in grooves) on their inner (female) or outer (male) surfaces designed to accept connections with matching threads. Threads which provide a simple connection but no seal are called straight threads. Tapered threads are designed to provide a tight seal for gases or fluids under pressure. Seal reliability can be improved by adding a coating or seal tape (Teflon). Especially precise threads are called "dry fit", meaning they seal without the need for an additional sealant, which is important in applications where sealant addition could cause contamination or corrosion. The thread size is measured and based on the inside of the vessel. Thread size standards include NPT (National Pipe Thread) and BSP (British Standard Pipe), though other standards exist and usage often varies by country and industry. Each standard corresponds to a particular number of threads per inch (TPI).
Gallery